Create Game/[Window API] Game Client & Game Server
[SERVER] Atomic
GameChoi
2023. 1. 5. 23:47
1. Atomic
1.1 Atomic
- 모든 쓰레드들이 수정 순서에 동의를 해야하는 경우는 바로 모든 연산들이 원자적일 때 가능
- 원자적인 연산이 아닌 경우
- 같은 수정 순서를 관찰할 수 있음이 보장되지 않음
- 직접 적절한 동기화 방법을 통해 처리
- 위 방식을 지키지 않을 시 프로그램이 정의되지 않은 행동을 함
1.2 Main
- atomic의 템플릿 인자로 원자적으로 만들고 싶은 타입 전달
- atomic 객체에서 제공하는 함수들을 통해 여러가지 원자적인 연산들 수행 가능
int main()
{
vector<std::thread> workers;
std::atomic<int> counter(0);
workers.push_back(std::thread(worker, std::ref(counter)));
workers.push_back(std::thread(worker, std::ref(counter)));
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) workers[i].join();
cout << counter << endl;
}1.3 worker
- mutex나 condition variable로 보호하지 않아도 counter의 값이 정상적으로 출력
void worker(std::atomic<int>& counter)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) counter++;
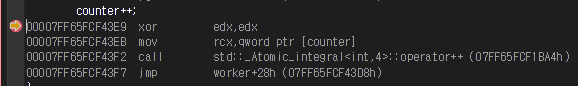
}- 컴파일러로부터 어셈블리 코드 분석
- atomic operator를 사용